Table of Contents
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Getting Started
- 3. Building Q/A Chat Bots
- 4. Integrating AI-Driven Chats
- 5. Human Operator Integration
- 6. Scripting for advanced features
- 7. Data Management
- 8. Advanced Features
- 8.1 Matching values and matching lists
- 8.2 Multi-Language Support
- 8.3 Discussions monitoring
- 8.4 Disk space cleaning
- 8.5 SSL certificates management
- 8.6 Chat bots servers
- 8.7 Chat bots clients authentication
- 8.8 Human operator’s registration
- 8.9 Messages text formatting
- 8.10 Chat bots params
- 8.11 Chat bots settings
- 8.12 Multiple AI models
- 8.13 Task bar icon
- 8.14 AI Groups
- 9. Global Settings
- 10. NoGUI Mode
- 11. Troubleshooting
- 12. Appendices
1- Introduction
Chat4Us is a chat flow creator and editor software that allows users to create and manage chat bots for various platforms. It provides a user-friendly interface for defining and testing chat flows, integrating AI models, and managing user data.
1.1 Overview of the Chat Bot Creator/Editor Software
Chat4Us is a software package that is designed to help users and companies easily manage chats with their customers through a chat client app or website integrated frame. The chat starts with a Q/A flow that is aimed at catching users queries then when needed it can be switched to an AI chat so as to the AI model can answer users questions and provide them with useful information. The chat can then be redirected to a human operator at any moment to handle complex cases like bookings, making orders and payments, etc.
1.2 Key Features and Capabilities
- Q/A Chat Flow: The chat bots editor lets you create and manage Q/A chat flows through a user-friendly interface. You add chat nodes and connect them together to build the flow and define the branching logic. You can define questions and answers, handle branching logic, and customize the response format.
- AI Mode: At any point in the chat flow, you can enable AI mode to switch to an AI driver chat. You can configure AI models and parameters to control the AI behavior. You can handle AI fallbacks and edge cases through scripts to ensure a smooth flow and handle the cases where users ask for an agent/operator help or wants to make an order…
- Agent/human operator Integration: To handle complex cases like bookings, making orders and payments, you can connect the chat flow to a human operator through the messenger app. You can define handover triggers to redirect the chat to the operator when needed.
- Data management: To store and retrieve user data, you can set up a local database and configure it to store user data. You can also connect to external APIs to load and store data. You can also use simple TXT/CSV files for simple tasks. Those features and other advanced ones are manageable using scripts.
- Multi-language support: Chat4Us supports multi-language chat bots creation and management. You can define and switch between different languages for the chat flow.
- Scripts: Advanced features like data management and remote API calls can be implemented using scripts. You can write custom scripts to handle specific use cases and handle edge cases.
1.3 Target Audience and Prerequisites
Chat4Us is intended for users who want to create and manage chat bots for their websites or apps. It is also suitable for companies that want to automate customer support, bookings, order management or internal helper chat bots for their employees.
There is no need for any programming knowledge or experience to create and manage chat bots using Chat4Us. On the other hand, it is recommended to have some knowledge of JavaScript programming language to write scripts for advanced features like data management, remote API calls and chat monitoring.
1.4 How to Use This Guide
You can use this guide to learn how to create and manage chat bots using Chat4Us. It provides step-by-step instructions on how to define chat flows, integrate AI models, handle agent/human operator integration, and manage user data. To save time and make chat bots creation task easier, please take time to read till the end.
2. Getting Started
Chat4Us is a lightweight cross-platform software that is easy to install and use. It is available for Windows, MacOS, and Linux operating systems. All packages are made in the “portable” way, you just need to extract the compressed package into a folder and start creating and managing chat bots using the user-friendly interface.
2.1 System Requirements
Chat4Us is compatible with Windows, MacOS, and Linux operating systems. It requires Java Runtime Environment (JRE) version 21 or higher to run. It is recommended to use the latest version of the JRE.
Chat4Us is a lightweight software that can run on any computer with a minimum of hardware requirements. If you are planning to use local AI models, it may require more hardware resources or run Chat4Us and AI models on separated servers.
2.2 Installation and Setup
Chat4Us packages comes on separated compressed packages.
- Chat4Us-Creator: The main package containing the chat bot creator and editor software. Extract the archive into a folder and grant execution permission to chat4us-creator-vx.x.x.jar file and other folders and files so that you can run the software.
- Chat4Us-Agent: The package containing the messenger app. If you are planning to use an agent/human operator integration, you will need to extract the archive into a folder and grant execution permission to chat4us-agent-vx.x.x.jar file and other folders and files so that you can run the software.
- Chat4Us-WebClient: The package containing the web client sample project that you can use as a template to integrate a chat bot in your own website, blog, etc. The archive contains a web project developed using HTML, CSS, JS and PHP that is a web page that contains an IFrame that will host the chat between users and the chat bot and/or human operators.
- Chat4Us-ClientApp: The package containing the java app sample project that you can use as a template to integrate a chat bot in your own desktop or mobile app. The Java project is made as simple as it is possible in order to be understandable and easy to port to other platforms like Android.
Major AI models like OpenAI, DeepSeek and Groq APIs integration are natively supported in Chat4Us. If you are planning to use local AI models like GPT4All, you will need to download and install them on your machine and configure them to work with Chat4Us. We will provide instructions on how to do that later in this guide.
2.3 User Interface Overview
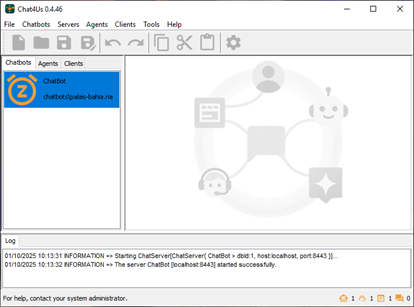
Chat4Us UI is made simple to use. The left panel of the main window is composed of 3 tabs that let you manage chat bot servers, agent/human operators and remote soft/web clients. The bottom panel shows log messages that you can monitor to ensure that the software is running smoothly.
The remaining area of the main window is where you can create and manage chat bots. Chat bots are edited by the graphical editor as a diagram where the chat flow is represented as nodes connected one to another. Each node represents a step in the chat flow.
The status bar contains live numbers of active servers, agents, clients and chats.
We will provide instructions on how to create and manage chat bots later in this guide.
3. Building Q/A Chat Bots
Q/A chat bots are the most common type of chat bots. They are used to catch users queries and provide them with answers based on predefined questions and answers. Each question is defined in the chat flow by a node in the diagram. The nodes are connected one to another to form the chat flow.
3.1 Defining Questions and Answers
Start by adding a new node in the diagram. Double click on it to open the node settings dialog. There, you can setup the question message, validation conditions then success/error messages and actions.
Continue by adding more nodes for the rest of the chat flow.
3.2 Branching Logic and Conditional Responses
When the nodes are fully defined, you can connect one to other ones using the green handle on success or red handle on error. Just click on the handle and drag it to the node you want to connect to. Nodes will be automatically connected when using Nodes settings dialog.
Save the chat bot diagram to a file and your chat bot is ready to be tested.
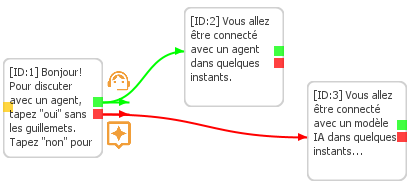
3.3 Customizing Response Formats (Text, Media, Buttons)
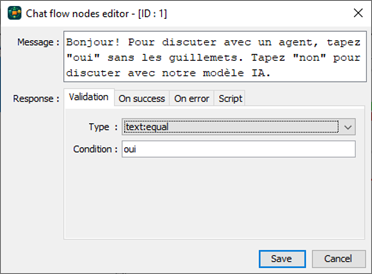
Chat bots messages can be customized using the Node Settings dialog. The advanced features like scripts and others will be covered later in this guide.
- Node message: The message that will be shown to the user.
- Validation tab: The conditions that will be used to validate the user input. This includes response type (text, number, etc.), operator (equal, interval, matching list, etc.).
- Success tab: The message that will be shown to the user if the user input is valid. This includes also the ID of the node to move to on success.
- Error tab: The message that will be shown to the user if the user input is invalid. This includes also the ID of the node to move to on error.
- Script tab: The script that will be executed on user response for the node. When defined the success/error actions are ignored and the script will validate the user input and move the user to the next node based on the script logic. The script can also switch to an AI driven chat or an agent/human operator based on the user input.
3.4 Testing and Debugging Q/A Flows
Once your chat bot flow logic is defined and saved to a file, you can test it using the web or software client. Your chat bot file needs to be connected to a chat bot server in order to be tested. Creating and managing chat bots servers is described later in this guide.
4. Integrating AI-Driven Chats
AI-driven chats are the most advanced type of chat bots. They are used to catch users queries and provide them with answers based on predefined questions and answers. Chat4Us supports multiple major AI models APIs like OpenAI, DeepSeek and Groq. You can also use local AI models like GPT4All or Ollama.
4.1 Configuring AI Models and Parameters
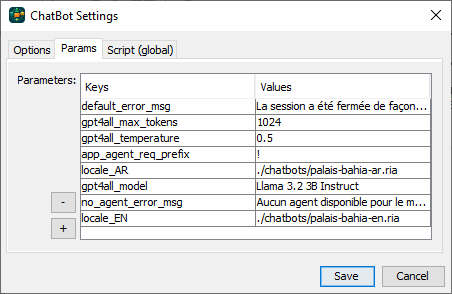
Before enabling AI mode you need to fill the AI model parameters. Right click on an empty space on the chat bot editor then select “Settings”. On the chat bot settings dialog, select Params tab and fill the Key/Values params table. Depending on each AI API, add the required params to the table with the AI model prefix (e.g. OpenAI: chatgpt_, DeepSeek: deepseek_, Groq: groq_, GPT4All: gpt4all_). For GPT4All: gpt4all_model, gpt4all_temperature, gpt4all_max_tokens are required to connect to GPT4All API server. Remote AI models APIs requires prefix_api_key to be defined in order to query the API server.
You need also to set the AI API url on the chat bot server dialog. Chat bot servers creation and management is described later in this guide.
4.2 Switching Between Q/A and AI Modes
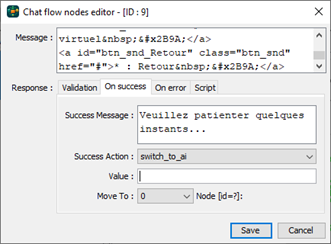
At any node of the chat flow, you can switch to AI mode by setting the success or error action to “switch_to_ai”. The AI mode will be active for the rest of the chat flow. You can switch back to Q/A mode by using the global script on the chat bot settings dialog which is and advanced feature that will be covered later in this guide.
4.3 Handling AI Fallbacks and Edge Cases
When the chat bot AI mode is active, the remote user will stay connected to the AI model for the rest of the chat session. You can use the global script on the chat bot settings dialog to monitor the AI/user discussion. During the global script execution, you can analyze AI/user messages and handle special case like discussion moderation and when needed switch the chat mode either back to Q/A to redirect the user to a booking/order chat flow, to a human agent for more complex cases or even abort the chat.
5. Human Operator Integration
To handle complex cases like bookings, making orders and payments, you can connect the chat flow to a human operator through the messenger app. You can define handover triggers to redirect the chat to the operator when needed.
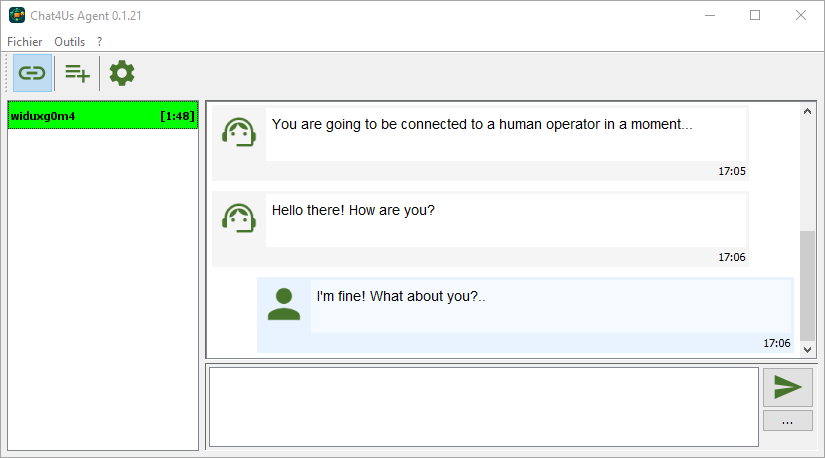
5.1 Setting up messenger app connections
Extract and configure the messenger app by extracting the archive chat4us-agent-vx.x.x.zip to a folder of the human operator computer, grant permissions when needed. Start the messenger app and click the “Connect” button on the toolbar so the app starts accepting connections from the chat bot server. When the chat bot server detects that a chat flow is redirecting a remote user to a human operator, it will connect to an available messenger app. When connected, the messenger app will show the chat discussion and let the human operator continue the chat.
5.2 Defining handover triggers
You can define handover triggers to redirect the chat to the operator when needed.
- On the node settings dialog, set success/error actions to “switch_to_agent”.
- During the global script execution by monitoring AI/user discussion.
- Define a guideline rule for the AI model to begin its response with a special prefix when it feels the need to redirect the chat to the operator. The guidelines and the prefix can be configured on the chat bot settings dialog. Options tab for the guidelines and Parameters tab then param key “app_agent_req_prefix” for the prefix.
5.3 Monitoring and managing live chats
Monitoring live chats is handled by the global script. Click on an empty area on the chat bot editor and select “Settings”. On the settings dialog, select Global Script tab then add the required code to monitor the AI/user discussion. The script editor will show 2 functions that will be called when the AI model or the remote user sends a message.
The chats are automatically saved to a file that you can find on the chats subfolder. You can check them out in order to update the chat flow logic if needed and also to see how the AI model is responding to the user so it can be fine-tuned when needed.
5.4 Operator tools and best practices
Human operators has the ability to add responses templates for most asked questions. Activate or deactivate sound notifications for incoming chats and more.
User messages have timeout counter running from when they were received. The connection with the remote user will be closed at the end of the timeout period.
Navigate to Chat4Us-Agent user guide for more details.
6. Scripting for advanced features
Chat4Us supports advanced features like data management and remote API calls. You can write custom scripts to handle specific use cases and handle edge cases. JavaScript is the programming language used to write and execute scripts.
6.1 Scripting overview
Some advanced features are implemented using JavaScript. The script editor supports syntax highlighting, line numbers and auto-completion. Scripts are used to handle user response within the node level and also within the global scope when the AI model is active.
6.2 Node script
The script that will be executed on user response for the node. When defined the success/error actions are ignored and the script will validate the user input. Open the node settings dialog, select Validation tab then select “script” as the Validation type. After that, select the Script tab and add the required code. The user message is available via the “response” global variable. See possible return values in the script API reference.
6.3 Global script
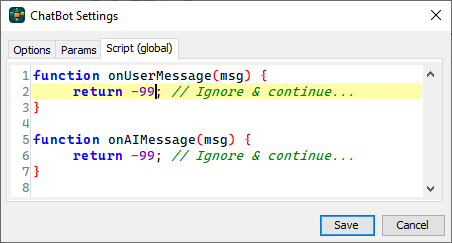
The script that will be executed on user response when the AI model is active. Right click on an empty space on the chat bot editor then select “Settings”. On the settings dialog, select Global script tab then add the required code. Write the callback functions to be called when the AI model or the user sends a message.
function onUserMessage(msg) { … } // Called whenever the remote user sends a message during any chat mode.
function onAIMessage(msg) { … } // Called when the AI model sends a response
6.4 Script API
The script code must return an integer value. The possible return values are:
- >=1: Move to the node with the specified id. An error is raised on error.
- 0: Repeat current node action.
- -1: End the chat.
- -2: Restart the chat bot.
- -3: Switch to AI mode.
- -4: Switch to Agent mode.
- <-4: NOP. No action.
The following is a list of available chat bot API functions:
Accessing remote API servers:
- String loadRemoteContentGET(String url);
Load content from a remote URL using a GET request. “url” param is to be set the remote server URL.
- String loadRemoteContentPOST(String url, Map params);
Load content from a remote URL using a POST request. “params” is a map of key/value parameters to send the remote server defined by the “url” param.
Local database management:
- Object[][] sqlQuery(String dbFile, String query, Object args);
Execute a SQL query on a local database file and return the results. “dbFile” is the relative path to the SQLite database that should be placed inside the chatbots folder or sub folder. “query” is the SQL query to execute. “args” is the list of query parameters.
- int sqlUpdate(String dbFile, String query, Object args);
Execute a SQL update on a local database file and return the number of affected rows. “dbFile” is the relative path to the SQLite database that should be placed inside the chatbots folder or sub folder. “query” is the SQL query to execute. “args” is the list of query parameters.
- int sqlInsert(String dbFile, String query, Object args);
Execute a SQL insert on a local database file and return the generated integer key. “dbFile” is the relative path to the SQLite database that should be placed inside the chatbots folder or sub folder. “query” is the SQL query to execute. “args” is the list of query parameters.
Text files I/O:
- boolean writeContentToFile(String filePath, String content, boolean append);
Write a string content into a file that is located inside the chatbots folder or sub folder. “filePath” is the destination file’s name and path. “content” is the content to write. “append”, append “content” to file when true or overwrite it when false.
- String readContentFromFile(String filePath);
Read entire content from a file that is located inside the chatbots folder or sub folder. “filePath” is the source file’s name and path.
- String loadCSVContent(String filePath, String keyword, int column, String separator, int limit);
Load data from a CSV file based on the “keyword” param. The file must be located inside the chatbots folder or sub folder. “filePath” is the source file’s name and path. “keyword” is the keyword to look for and return lines that contain it. “column” is the index of the column to check for the keyword. “separator” is the columns separator. “limit” is the max number of columns to return, the remaining will be ignored.
6.5. Scripts templates:
Here is a script template that you can use on a chat flow node’s scope. Variable “message” content is the text that will be sent to the remote user. You can use a global variable “response” that contains remote user message.var message = “Initital node’s message”;
function main() {
…
message += "Append a result";
return value ; // See return values described earlier
}
main();
Here is a script template that you can use on a global scope. onUserMessage is called whenever the chatbot server receives a remote user message. onAIMessage is called whenever a connected AI model generates a response that is aimed to the remote user. “msg” param contains user or AI model message and you can overwrite it by affecting a content to the global variable “message”.function onUserMessage(msg) {
return value; // See return values described earlier
}
function onAIMessage(msg) {
return value; // See return values described earlier
}
7. Data Management
During the chat flow you can store and retrieve user data using global variables and local files and databases.
7.1 Global Variables
To define a global variable, open the node settings dialog then select “variable:user_value” as the success/error action and finally set “Value” as the variable name. When the node is executed the variable will be created and filled with the user response.
You can access the variable later in the chat flow by including the variable name in the node message or success/error messages like this: {:var_name:}. You can access the variable later in the node or global script by including the variable name.
7.2 TXT & CSV local files
TXT and CSV files can be used to store user data beside the RIA chat bot file and sub folders using nodes/global scripts. You can use the readContentFromFile and writeContentToFile functions to load/store contents from/to local files. You can also use the loadCSVContent function to load data filtered by a keyword from CSV files. Please refer to the Script API section for more details.
7.3 Local Database
SQLite databases can be used to store user data. Start by creating a SQLite database file using a third-party tool then copy it to the same folder as the chat bot file. SQLite databases can be accessed only inside nodes/global scripts using sqlQuery, sqlUpdate and sqlInsert functions covered in the Script API section.
7.4 Remote data management
You can use the loadRemoteContentGET and loadRemoteContentPOST functions to load/store contents from/to remote servers. See the Script API section for more details. The methods provided by these functions are used as is and you should consider the security implications of loading untrusted APIs from a server. When making HTTP requests to external servers, it’s essential to check if they offer HTTPS encryption, which can help protect sensitive information being sent or received over the network.
8. Advanced Features
Chat4Us offers a range of advanced features that assist in bot management, from built-in tools to more intricate edge cases handled through scripting. This chapter explores the most commonly employed advanced functionalities for building and managing chat flows.
8.1 Matching values and matching lists
Matching values are used when we need to convert user input to specific values. For example, when we ask the user to enter the language that he wants to switch to:
[‘English’,’EN’][‘French’,’FR’][‘German’,’DE’][‘Back’,1]
Where ‘English’ is the user response and ‘EN’ is the matching value that is passed to the chat bot logic to change current language to English. The last matching values entry moves to node id=1 when the user response is ‘Back’.
Matching lists are key/values list that is used to validate user input and move the user to other places in the chat flow. It can also be used to switch to the AI mode or to redirect the user to a human operator.
Matching lists has the following format: [‘key1’, value] where key1 is the expected user response and value can be one of the following values:
- >=1: Move to the node with the specified id.
- 0: Repeat current node action.
- -1: End the chat.
- -2: Restart the chat bot.
- -3: Switch to AI mode.
- -4: Switch to Agent mode.
- <-4: NOP. No action.
No need to mention that matching lists values are the same as the scripts expected return values.
8.2 Multi-Language Support
Chat4Us supports multi-language chat bots creation and management. You can define and switch between different languages for the chat flow. Switching between languages is easy to implement and doesn’t require to be done using scripts. Follow these steps to create a multi-language chat bot:
- For each language you need to create a separate chat bot flow file.
- In the main chat bot file, right click on an empty area and select “Settings”. On the settings dialog, select Options tab and define the main Locale. On the Params tab table, add different languages chat bots files you created: Key: locale_XX and value: relative_path_to_chat_bot_file where XX is the language code. Ex: locale_EN – ./chatbots/my-chatbot-en.ria
- Add a node to the chat flow that asks the user to switch to one of the defined languages. Use a matching values to redirect the user to the corresponding chat bot file. Ex: [‘English’,’EN’][‘French’,’FR’]
- You may need this node in every chat bot specific language to let users switch back to the main language.
8.3 Discussions monitoring
Discussion monitoring is an important feature that allows you to monitor and manage AI models/users discussions. Chat4Us lets you monitor discussion in two different ways:
- Real time monitoring: Using the global script lets you monitor the AI/user discussion in real time either for moderation purposes or to handle edge cases like when the user is at the point of making an order, a booking or asking for human support. Check out the Script API section for more details.
- Discussions history: You can access the history of users discussions saved into the chats subfolder. Monitoring saved chats should be part of your regular maintenance routine especially when AI models and human operators are involved. Checking chats history lets you find out how the AI model is responding and fine tune it when needed. It may also let you check most common users questions and provide accurate responses to them.
8.4 Disk space cleaning
Chat4Us maintains numerous files containing vital information in its chat and log sub-folders. Over time, these files can accumulate significantly, occupying substantial disk space. To address this issue, Chat4Us offers a cleaning feature to remove outdated files.
To clean up the disk space, start by defining the maximum log/chat files duration in the Settings dialog >> Misc tab. Then you can at any moment choose from the main menu Tools >> Clean >> Saved chats or Tools >> Clean >> Log files.
8.5 SSL certificates management
Chat4Us uses SSL certificates to secure the connection between the API server and the clients. You can either create a self-signed certificate or import an external one. Remember that the new password will be required to authenticate the next time you run Chat4Us. Remember also the current running chat bot servers will continue using old certificates until you restart Chat4Us.
- Self-signed certificates: Choose from the main menu Tools >> Security >> Regenerate self-signed certificate. The Certificate Generator dialog will appear where you can fill the certificate details. You need to enter current password and a new one to generate a self-signed password protected certificate.
- Import external certificate: Choose from the main menu Tools >> Security >> Import external certificate. The Certificate Importer dialog will appear where you can select the external certificate file to import. You need to enter current password and a new one to import the certificate.
8.6 Chat bots servers
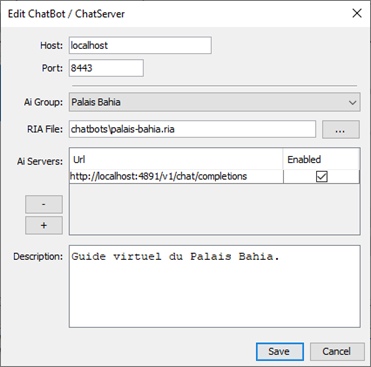
Chat4Us offers advanced chat bot server creation and management capabilities, allowing clients to connect remotely and engage in discussions through a web-based platform or a software client. These chat bot servers enable users to interact with either Q/A flows, AI models, or human operators via the messenger app. When creating a new chat bot server, you need to attach a pre-designed RIA file created prior using Chat4Us’s editor, enabling seamless execution of tailored interactions and conversations.
To create a new chat bot server, select Servers tab from the left panel, right click on an empty area and choose “Add…” from the pop up menu. Enter in the New chat bot server dialog, the host and the port number of the new server, select a chat flow RIA file. If the chat flow implements AI driven chats, then add the URL to the AI model/service in the AI Servers table. Save and the new chat bot server will appear inside the list inside the Servers tab. If not already running, right click on it and choose “Activate” from the popup menu. Use a soft/web client to connect to it and run the chat flow.
8.7 Chat bots clients authentication
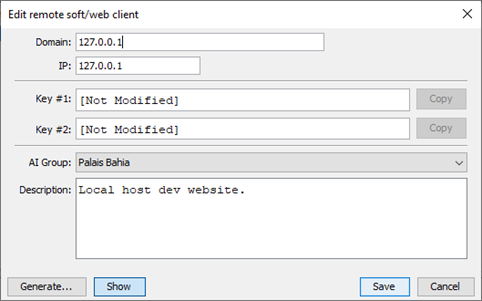
Chat bots clients either web or software must be authenticated to connect to the chat bot servers. To register a new client, choose Clients tab from the left tabbed pane, right click on an empty area and select “Add…”. On the New client dialog, enter the client details especially the Key #1 and Key #2 which the client must provide in order to connect to the chat bot server. For clients authentication logic, please refer to the sample web/java projects that come with Chat4Us.
8.8 Human operator’s registration
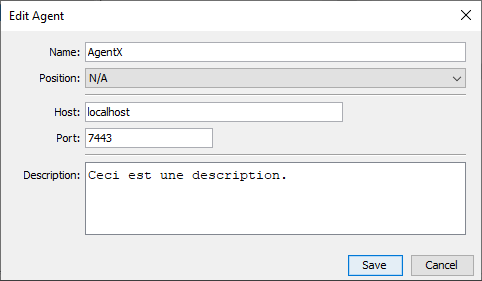
Chat4Us allows you to register human operators to the chat bot servers. Human operators are users that uses the messenger app chat4us-agent to handle complex cases like bookings, making orders and payments. You need to register human operators so chat bots servers can know their existence and their IPs & ports to connect to the messenger apps running on their machines.
To register a new human operator, Choose Operators tab from the left tabbed pane, right click on an empty area and select “Add…”. On the New operator dialog, enter the operator details especially the host/ip address and port number of the messenger app running on the operator machine.
8.9 Messages text formatting
When designing chat bots you should pay attention to text formatting. If you are planning to run it on a web client, you can format messages text using CSS classes that is defined on the web client CSS files. On the other hand you need other design pattern when running the chat bot on a mobile or desktop app. This is very important especially when chat bot messages implement clickable menus or buttons and also when it may contain multimedia contents.
8.10 Chat bots params
Chat4Us supports multiple chat bot params that can be used to personalize the chat flow. These params can be defined in the chat bot settings dialog. Here is a list of the available params:
- locale_XX: Used to let chat servers locate different RIA files for different languages. It is usually used when creating a multi-language chat bot. Ex: locale_EN – ./chatbots/my-chatbot-en.ria
- default_error_msg: Used to let chat servers display a default error message when an error occurs. It is used to provide language specific error messages for multi-language chat bots.
- no_agent_error_msg: Used to let chat servers display a default error message when no agent/human operator is available. It is used to provide language specific error messages for multi-language chat bots.
- app_agent_req_prefix: Used so the AI model can begin its response with a special prefix when it feels the need to redirect the chat to the operator. You can add a query in the AI guidelines to fulfill this purpose. You can also use global script to check the AI model or user response and redirect the chat to the operator when needed.
- AI API params are covered earlier in this guide.
8.11 Chat bots settings
Chat4Us supports multiple chat bot options that can be used to personalize the chat flow.
- Name: Chat bot name.
- Locale: Chat bot locale ex: AR, EN, FR.
- Guidelines: AI model guidelines when implementing AI-driven chats. Here you define the rules that the AI model must follow during the AI driven chats.
8.12 Multiple AI models
When creating a new chat bot server, you find that “AI Servers” can hold many AI models URLs. This is useful when you want to connect a chat bot server to multiple offline/local AI models at the same time to balance their load over multiple chat bot servers. You can enable/disable each AI model using the checkbox next to its URL. Ex: disable an AI model for maintenance purposes while leaving the others enabled.
8.13 Task bar icon
Chat4Us creates an icon on the task bar at startup, it serves many purposes:
- Double click on it to show the main window. This is important especially if you activate “Minimize to task bar icon” on the Settings Dialog.
- Right click to show the popup menu where you can either show the settings dialog or quit the program.
8.14 AI Groups
One of the most advanced features of Chat4Us is the AI Groups. Things may become very complex when creating many chat servers, agents and clients. Separating chat servers and connected agents and clients into groups may let you better manage Chat4Us and its components. A running chat server will only accept connections from messenger apps and soft/web clients that are in the same group.
First start by adding a new AI group into the list under Settings Dialog >> AI tab then affect desired chat bot servers, agents and clients that are meant to connect to each other in their respected new/edit dialogs.
Global Settings
You can find global settings on the main menu Tools >> Settings. It holds all global settings that apply to all running servers and its behaviors towards web/soft clients and messenger apps.
9.1 Misc tab
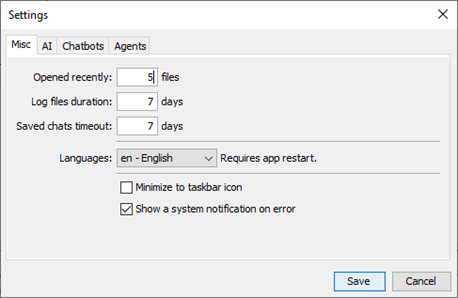
Misc tab is used to define the maximum log/chat files duration, the maximum number of chat files to keep in the log and chat folders, the number of recently opened files to keep in the main menu and there you can change Chat4Us UI language. There also, you can change normal behavior of the main window to minimize on the taskbar icon which you can double click to show it again. When needed, you can check “Show a system notification on error” to monitor severe errors when the main window is not visible or on the background.
9.2 AI tab
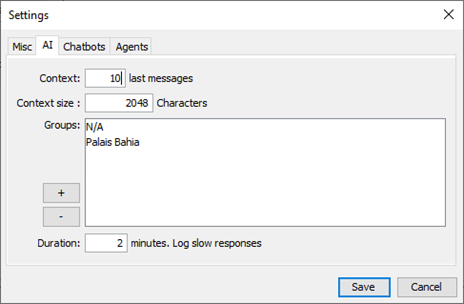
AI tab is used to define AI params and options. Here is a list of the available AI settings:
- Context messages: Number of last messages to include within each AI request so as the AI model takes into consideration discussion context when generating next response. Remember that the high this value the high input tokens are and response generation machine load is high for local/offline AI models.
- Context Size: Maximum number of characters that an AI request can contain. Same remark about high tokens and machine resources load.
- AI groups: Each chat bot server you create can be part of an AI group. AI groups are used to group chat bots that share same interests. Add groups that will be available when creating a new chat bot server or affecting an agent/human operator.
- AI model slow responses duration: Log a message when the AI model takes longer than this duration to respond to a message. This is useful when you want to monitor the AI model performance, especially when using local AI models like GPT4All that need a lot of processing power.
9.3 Chat bots tab
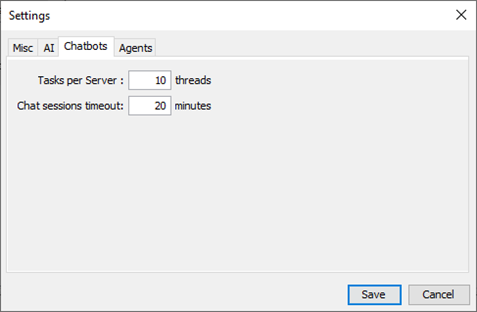
Chat bots tab is used to define chat bot params and options. Here is a list of the available chat bot settings:
- Tasks per server: Number of concurrent AI tasks per chat bot server. This is used to limit the load on the chat bot server and the AI model. Pay attention that timeouts can cause disconnections from remote users.
- Chat sessions timeout: Number of minutes before the chat session is disconnected when no interaction from the remote user.
9.4 Agents/Operators tab
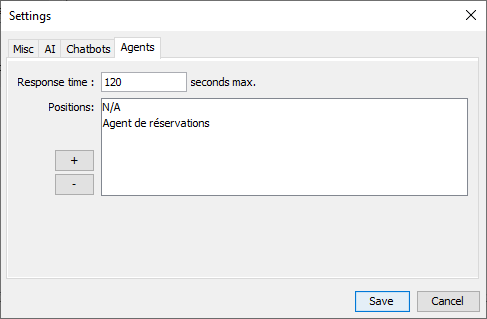
Agents/Operators tab is used to define agent/human operators params and options. Here is a list of the available settings:
- Max response time: Maximum number of seconds that chat bots servers will wait before disconnecting from a messenger app. If the agent/operator does not reply within the timeout, the chat/remote user session will be disconnected. Timeout usually is 120 seconds but can be edited here.
- Agent/Operator position: Each agent/human operator you add can have a position. This is used to group agent/human operators that share same specific skills that are required for specific cases.
10. NoGUI Mode
Overview
The NoGUI (Non-Graphical User Interface) mode is a headless operating mode designed for environments where a graphical desktop is unavailable or unnecessary. This mode allows you to run Chat4Us-Creator as a service, API server, or command-line tool, making it ideal for server deployments, Docker containers, automation scripts, and remote administration.
This section assumes you have a solid understanding of how Chat4Us-Creator GUI mode works. NoGUI mode is designed for advanced users who need to host chatbots in headless environments and are comfortable using Bash, PowerShell, and other system command-line interfaces.
Chat flow design and RIA files edit functionalities are not implemented in the NoGUI mode. You still need the GUI default mode to design and edit chatbots. Without the GUI mode, the advanced design and editing tools associated with chatbot design and development are unavailable.
10.1. Use Cases
- Server Deployment: Run as a persistent chatbot API server on headless Linux servers
- Remote Administration: Manage chatbots via command-line interface over SSH
- Automation: Integrate with scripts and DevOps pipelines
- Resource-Constrained Environments: Reduce memory and CPU usage by eliminating GUI overhead
10.2. Starting in NoGUI Mode
Basic Startup Options
# Standard GUI mode (default)
java -jar chat4us-creator.jar
# NoGUI Server mode
java -jar chat4us-creator.jar --nogui
# Bash script to run NoGUI Server mode in background
./chat4us-server.sh
# NoGUI CLI Client mode
java -jar chat4us-creator.jar --nogui --cli
# Or
./chat4us-cli.sh
# Custom port configuration
java -jar chat4us-creator.jar --nogui --port 1985
# SSL certificate import. Requires defining a new authentication password.
java -jar chat4us-creator.jar --nogui --cert cert.crt --key key.key --alias my_cert
Authentication
When initiating in NoGUI mode, it will prompt for password authentication to access the PFX keystore containing the SSL certificate and private key, allowing the server to run and securely serve clients, agents and CLI queries over HTTPS. The default password to be used after installation is: a123456/*
Note: Keep your password secure. If lost, you cannot authenticate to grant access to Chat4Us-Creator Server and CLI.
10.3. NoGUI Server Mode
Overview
In server mode (–nogui without –cli), Chat4Us-Creator runs as a headless service that:
- Hosts chatbot instances
- Processes remote client connections
- Maintains conversation states
- Provides administration via the command line CLI (–cli)
10.3.1 Server Commands Reference
Once the server starts, you can manage it through the command interface CLI. The server accepts the following commands:
Basic Administration
- status – Display server operational status
- metrics [summary] – Show performance metrics (add ‘summary’ for condensed view)
- log-tail [nLines] – View recent last log entries (default: 10 lines)
- cert-info – Display certificate information and expiration status
- help – List all available server commands
- exit – Shut down the server gracefully
Listing Resources
- list bots – Show all configured chatbots
- list agents – List registred human agents (messenger apps)
- list clients – Display registered remote clients
- list ai_groups – Show AI group configurations
- list ai_servers – List all LLM servers
- list positions – Display agent position definitions
Chatbot Management
- bot-test <botId> – Open internal test client for quick chatbot tests. Will not work in headless environments.
- bot-info <botId> – Display detailed chatbot configuration
- bot-metrics <botId> [summary] – Show chatbot performance metrics
- bot-new <host;port;ria_file;context_size;ai_group_id;description> – Create new chatbot. Arguments are ‘;’ separated and all required.
- bot-edit <botId> <id=?>;<host=?>;<port=?>;<ria_file=?>;<context_size=?>;<ai_group_id=?>;<description=?> – Modify existing chatbot. Provide fields to edit only.
- bot-enable <botId> <yes|no> – Enable/disable chatbot
- bot-start <botId> – Start chatbot server
- bot-restart <botId> – Restart chatbot (disconnects clients)
- bot-remove <botId> – Delete chatbot (disable first)
LLM Server Management
- bot-llm-add <botId> <url> <type> – Add LLM server to chatbot (types: ollama, gpt4all, chatgpt, groq, deepseek)
- bot-llm-remove <botId> <llmId> – Remove LLM server from chatbot
- bot-llm-enabled <botId> <llmId> <yes|no> – Enable/disable specific LLM server
Client Management
- client-info <cltId> – Show client details
- client-new <domain;ip;ai_group_id;key1;key2;description> – Register new remote client. Arguments are ‘;’ separated and all required.
- client-edit <cltId> [domain=?];[ip=?];[ai_group_id=?];[key1=?;key2=?];[description=?] – Modify client configuration. Provide fields to edit only.
- client-enable <cltId> <yes|no> – Enable/disable client access
- client-remove <cltId> – Remove client registration
Agent Management
- agent-info <agentId> – Display agent information
- agent-new <name;ip;port;pos_id;ai_group_id;description> – Create new agent. Arguments are ‘;’ separated and all required.
- agent-edit <agentId> [name=?];[ip=?];[port=?];[pos_id=?];[ai_group_id=?];[description=?] – Modify agent settings. Provide fields to edit only.
- agent-enable <agentId> <yes|no> – Enable/disable agent
- agent-remove <agentId> – Delete agent record
AI Group Management
- ai-group-new <label> – Create new AI group
- ai-group-remove <aigId> – Delete unused AI group
Position Management
- position-new <label> – Create new position definition
- position-remove <posId> – Remove unused position
Maintenance
- cleanup logs – Remove old log files
- cleanup chats – Clear expired chat sessions
- cleanup database – Remove unused database records
10.4. NoGUI CLI Client Mode
Overview
CLI Client mode (–nogui –cli) provides a command-line interface to:
- Connect to a running Chat4Us-Creator headless server
- Send queries (server commands) to the server
- Receive responses in console format
Client Commands
- /clear – Clear the console screen
- /about – Display client version information
- /help – Show available commands
- /exit – Disconnect and exit the client
Usage Example
# Start CLI client (default connects to localhost:1979)
java -jar chat4us-creator.jar --nogui --cli
# Or
./chat4us-cli.sh
# Start CLI client with custom port
java -jar chat4us-creator.jar --nogui --cli --port 1985
Once connected, you can interact directly with the server through commands. Use the slash commands for client control.
10.5. SSL Certificate Management
Importing SSL Certificate
java -jar chat4us-creator.jar --nogui --cert server.crt --key server.key --alias my_domain
This command:
- Prompts for PFX keystore password. Default : a123456/*
- Validates the certificate and private key
- Imports them into the application keystore
- Makes the certificate available for secure connections
Certificate Requirements
- Certificate and key must be in PEM format
- When prompted for certificate password, enter empty password for unencrypted private key.
- After import, restart Chat4Us-Creator server and CLI to use the new certificate
Port Configuration
- Default command port: 1979
- Custom port: –port <port_number>
- Chatbot servers use their own ports as configured in bot settings
- Ensure firewall rules allow traffic on configured ports
10.6. Troubleshooting
Common Issues
Password Authentication Failed
Ensure you’re using the correct PFX keystore password. You’ll need to define a new password when importing a new certificate.
Port Already in Use
- Check if another instance is running: netstat -tulpn | grep 1979
- Use –port to specify an alternative port
Certificate Import Errors
- Verify certificate and key files are in PEM format. Provide the passphrase when prompted if the private key is password-protected; otherwise, enter an empty password.
- Check file permissions.
Cannot Connect to Server
- Verify server is running: status command
- Check firewall settings
- Confirm port number matches
Logs and Diagnostics
- Use log-tail command to view recent logs
- Default log location: logs/ directory in application folder
10.7. Best Practices
Security
- Use strong PFX keystore passwords
- Regularly update SSL certificates
- Restrict server access with firewall rules
- Use separate credentials for production environments
Performance
- Monitor with metrics commands regularly
- Use cleanup commands to remove old data
- Adjust JVM memory settings for your workload: -Xmx2G -Xms512M
Backup
Regularly back up the settings.cfg configuration file and the chat4us.db file, which contains chatbots and related components.
Monitoring
- Use status and metrics for health checks.
- Monitor log files for potential errors or unexpected behaviors.
- Monitor saved chats for unexpected chat flow behaviors and inaccurate LLM responses.
10.8. Version Notes
- NoGUI mode introduced in version 0.6.0
- All subsequent versions maintain backward compatibility
- New commands may be added in future versions (check help for current list)
- Report bugs and issues via the project’s GitHub repository or here.
This NoGUI mode provides full functionality equivalent to the GUI version, enabling enterprise deployments, automated management, and scalable chatbot hosting without graphical interface dependencies. GUI mode is still needed for chatbots design and development.
11. Troubleshooting
The following is a list of common issues and their solutions. This document will be updated over time to include new issues and solutions. Don’t hesitate to contact us for issues reporting or feature requests. mailto:nospam.rida[at]gmail.com
11.1 Common Issues and Solutions
- Running Chat4Us on a slow machine beside a local AI model like GPT4All may cause performance issues especially AI model response timeouts that will cause immediate disconnection from remote users. Chat4Us and offline AI models like GPT4All are meant to run on separated machines unless it is fast enough to handle the load.
- Messages sent to human operators/messenger apps has defined timeout, usually 2 minutes. If the human operator/messenger app does not reply within the timeout, the discussion with the remote user will be disconnected. Operators must disconnect their messenger app when they are busy or not able to respond so as to the chat bot servers can connect to only available ones.
- Discussion with a remote user will be disconnected when no human operator is available to handle it ie: none of the registered messenger apps is running or accepting remote chat bots servers connection.
- When a chat bot server is no longer responding to chat clients, try disabling then enabling it. If the server is still not responding, Exit and rerun Chat4Us.
11.2 Errors reporting
When an unexpected error occurs, you’ll receive a dialog with detailed information about the issue. To assist our support team in resolving the problem, please click on the report button and add any additional details that will aid in fixing and updating Chat4Us.
11.3 Updating Chat4Us
Choose Check for updates… from the Help menu, this will open the download page, check for installed version and advise you to download and install the new version.
12. Appendices
Appendix A: Glossary of Terms
- Chat bot server: A web server that is connecting remote users through soft/web clients to chat flows that can be at a given time either a Q/A chat flow, AI-driven or human discussion by providing dedicated API interface to them.
- Chat bot diagram: The chat flow graphical representation in the graphical editor. The chat bot file is encoded in XML format and has RIA as extension when saved.
- Chat bot flow: The chat flow is the sequence of nodes that define the conversation between the chat bot and the remote user. The chat flow is represented in the chat bot diagram by nodes connected one to another.
- RIA: RIA is the default chat bot file extension and sometimes in this guide, chat bots files are mentioned as “RIA files”.
- Node: A node is a chat flow element that defines a specific message to the remote user, its validation logic and its actions for success or error.
- Script: The script is a piece of JavaScript code that is executed to handle advanced and edge cases. Scripts are powered with the ScriptEx class that adds specific API for Chat4Us features. It is covered earlier in this guide.
- Node script: The script that will be executed on user response for the node. When defined the success/error actions are ignored and the script will validate the user input and move the user to the next node based on the script logic. The script can also switch to an AI-driven or agent chat based on the user input.
- Global script: The script that will be executed on an AI model message or user response. It is essential for discussions monitoring and handling special cases.
- Remote user: The user that is connected to a chat bot server using either a web or software client.
- Agent/human operator: The user/employee that uses the messenger app to handle complex cases like bookings, making orders and payments…
- Messenger app: The app that is registered on Chat4Us and is used by human operators to take over discussions that need human interaction.
- AI model: The local or remote model that is used by the chat bot to answer user questions and provide them with useful information. Currently, Chat4Us supports GPT4All as local mode and ChatGPT, DeepSeek and Groq as remote models.
Appendix B: Keyboard Shortcuts
Global shortcuts:
- Ctrl+N: Create a new empty chat bot diagram in the editor.
- Ctrl+O: Open an existing chat bot diagram in the editor.
- Ctrl+W: Close the current chat bot diagram in the editor.
- Alt+F4: Quit Chat4Us.
Diagram editor shortcuts:
- Ctrl+S: Save the current chat bot diagram.
- Ctrl+Z: Undo the last action.
- Ctrl+Y: Redo the last action.
- Ctrl+X: Cut the selected node.
- Ctrl+C: Copy the selected node.
- Ctrl+V: Paste the copied node.
- Ins: Insert a new node.
- Del: Delete the selected node.
- F2: Edit the selected node.
